What if a tiny butterfly-shaped gland in your neck could be the reason behind your unexplained fatigue, mood swings, or sudden weight changes?
Millions of people walk around daily unaware that their thyroid gland is either working overtime or lagging behind—silently wreaking havoc on their health. Often dismissed as stress, aging, or “just one of those things,” thyroid symptoms can be subtle but serious. Ignoring them can lead to long-term complications.
Did you know? Women are up to 8 times more likely than men to develop thyroid disorders—yet it’s commonly underdiagnosed.
Doctors agree: when your thyroid speaks, it’s time to listen. Here are the top 10 symptoms that you shouldn’t ignore—and why early detection is key.

Do’s and Don’ts for Thyroid Health
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Get your thyroid levels tested regularly | Ignore persistent symptoms like fatigue or weight changes |
| Take prescribed medications exactly as directed | Skip or adjust thyroid medication without consulting your doctor |
| Eat a balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc | Consume excessive goitrogenic foods (e.g., raw broccoli, soy) |
| Stay hydrated and get enough sleep | Overdo caffeine or alcohol |
| Manage stress through yoga, meditation, or deep breathing | Stay in constant stress, which can worsen thyroid imbalance |
| Exercise regularly (moderate intensity) | Push yourself to extreme workouts if feeling fatigued |
| Use iodized salt in moderation | Take iodine supplements without medical advice |
| Monitor your weight, energy levels, and menstrual cycles | Rely solely on supplements to manage thyroid conditions |
| Inform your doctor of all current medications and supplements | Mix thyroid medications with high-fiber meals or calcium/iron supplements |
| Follow up on symptoms like neck swelling, palpitations, or hoarseness | Assume thyroid symptoms are just aging or temporary stress |
1. Unexplained Weight Gain or Loss
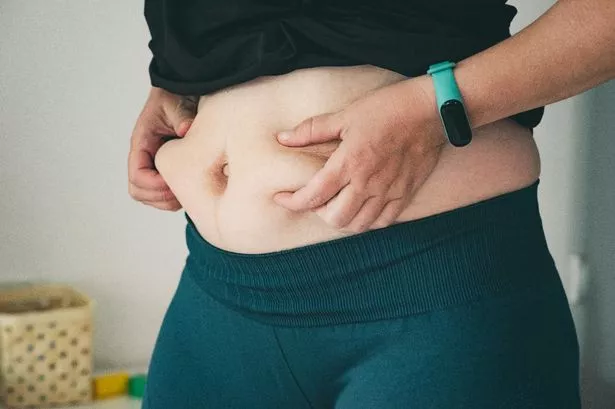

Suddenly gaining or losing weight despite no change in diet or activity? It’s a red flag.
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid): slows your metabolism, leading to weight gain.
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid): speeds it up, often causing weight loss.
Myth Buster: It’s not always about calories in vs. calories out. If your thyroid isn’t balanced, your metabolism won’t be either.
What to Do:
- Consult your doctor for a thyroid function test. If hypothyroidism is diagnosed, doctors typically prescribe synthetic thyroid hormone (levothyroxine).
- Diet and exercise may need to be adjusted based on your thyroid condition. With hypothyroidism, focus on a nutrient-dense, low-calorie diet to manage weight.
- For hyperthyroidism, treatment may involve antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery to remove part of the thyroid.
2. Persistent Fatigue or Sluggishness
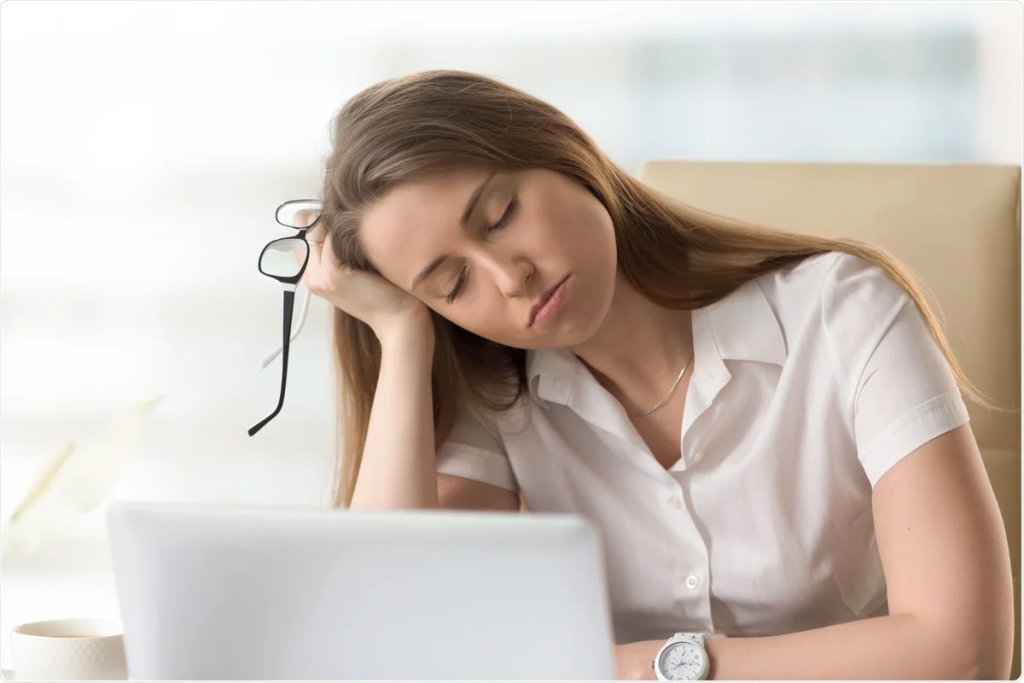

Feeling tired even after a full night’s sleep?
This isn’t just ordinary exhaustion.
- A sluggish thyroid reduces cellular energy production.
- You may feel mentally foggy, physically drained, or even depressed.
Interesting Fact: The thyroid influences brain function. In fact, many people with hypothyroidism report memory problems or “brain fog.”
What to Do:
- Thyroid hormone replacement: For hypothyroidism, levothyroxine can help bring your energy levels back to normal.
- Lifestyle changes: Ensure you get enough sleep, manage stress, and maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that support thyroid health (e.g., selenium, and zinc).
- Exercise regularly to combat tiredness and improve energy levels, but listen to your body and avoid overexertion.
3. Mood Changes and Anxiety
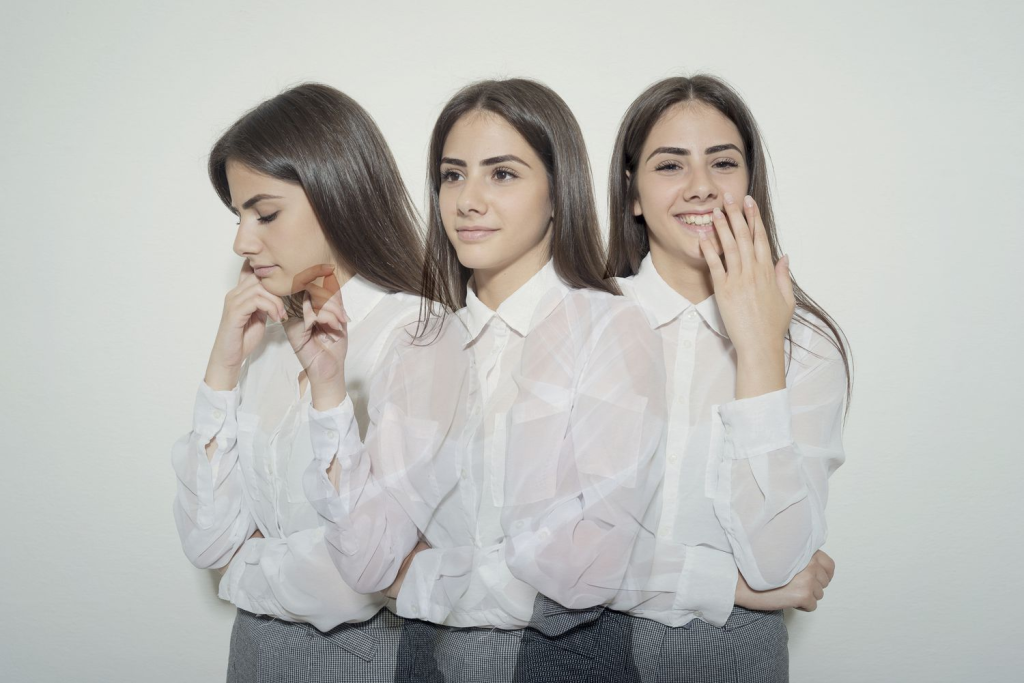

Mood swings, irritability, or unexplained anxiety might be more than emotional stress.
- Hypothyroidism is linked to depression and low motivation.
- Hyperthyroidism can cause restlessness, panic attacks, or mood instability.
Doctor’s Insight: Your thyroid helps regulate serotonin and dopamine—chemicals that directly impact mood.
What to Do:
- Thyroid treatment: Adjusting thyroid medication can stabilize your hormones and improve mood swings or anxiety.
- Psychotherapy or counseling: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or talk therapy can help you manage anxiety symptoms that might stem from thyroid imbalances.
- Stress management: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises.
4. Hair Thinning or Hair Loss
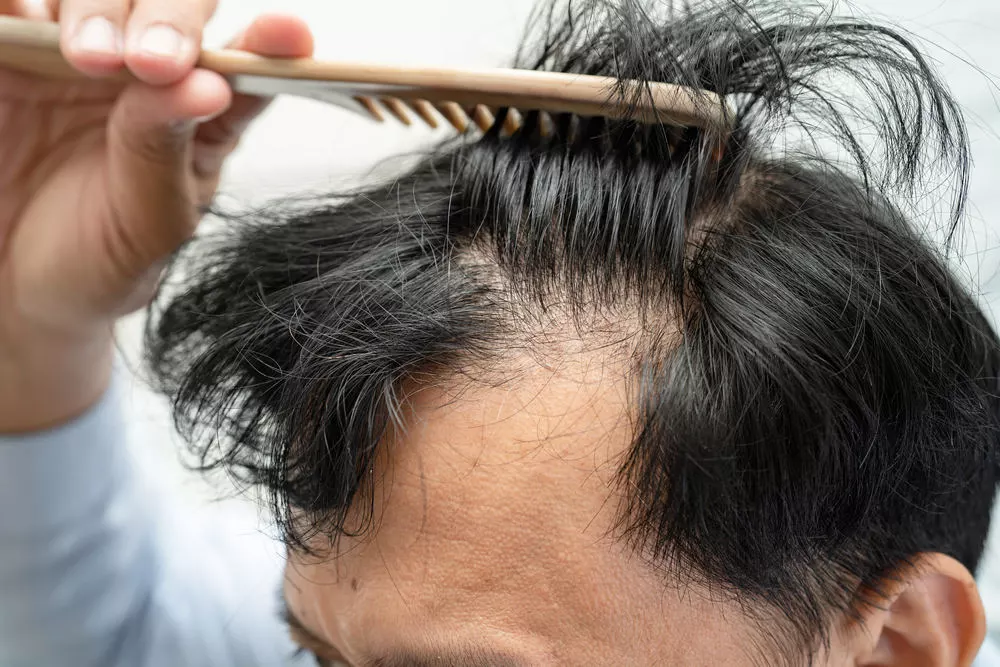

Losing more hair than usual?
It may not be just seasonal shedding.
- Low thyroid levels can force hair into a resting phase, leading to noticeable thinning, especially on the scalp and eyebrows.
- Nails may become brittle too.
Did you know? Eyebrow thinning, particularly on the outer third, is a classic thyroid symptom.
What to Do:
- Thyroid hormone optimization: Ensure your thyroid levels are balanced through appropriate treatment. Hair loss often improves once thyroid hormones are corrected.
- Topical treatments: Products containing minoxidil can help with hair regrowth, but they should be used with your doctor’s guidance.
- Protein-rich diet: Healthy hair requires a balanced diet rich in protein, biotin, and iron to support hair follicle strength.
5. Sensitivity to Cold or Heat

Are you always cold—even when others aren’t? Or do you sweat excessively?
- Hypothyroidism makes you cold-sensitive.
- Hyperthyroidism leads to heat intolerance and excessive sweating.
Why it matters: The thyroid controls your body’s internal thermostat. When it’s off, your comfort level follows suit.
What to Do:
- Thyroid medication: If hypothyroidism is the cause, proper thyroid hormone replacement will help restore normal body temperature regulation.
- Dress appropriately for your body’s new sensitivity. Layer up in cold weather and wear breathable fabrics if you’re feeling overheated.
- Monitor thyroid levels regularly with your healthcare provider to ensure they’re within a healthy range.
6. Irregular or Heavy Periods
Thyroid hormones are intricately linked to reproductive health.
- Hypothyroidism can cause heavy, prolonged periods.
- Hyperthyroidism may lead to lighter or missed periods.
Doctor’s Note: Irregular cycles can sometimes be the first visible sign of a thyroid disorder in women—especially if accompanied by fatigue or mood swings.
What to Do:
- Thyroid treatment: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt your menstrual cycle. Addressing thyroid function can often restore menstrual regularity.
- Hormonal therapy: If thyroid treatment doesn’t resolve menstrual issues, hormone therapy may help regulate your cycles.
- Nutritional support: Ensure a diet rich in essential nutrients like iron (especially if you have heavy periods) to avoid anemia.
7. Constipation or Diarrhea

Your digestive rhythm says a lot about your thyroid:
- An underactive thyroid slows digestion, often causing constipation.
- An overactive thyroid may lead to frequent or loose stools.
Tip: If your bathroom habits have shifted significantly without dietary changes, your thyroid could be the reason.
What to Do:
- Thyroid medication: If hypothyroidism is the issue, treatment with thyroid hormone replacement often relieves constipation. Hyperthyroidism may require treatment to slow bowel function.
- Fiber intake: Increase dietary fiber if constipation is an issue (for hypothyroidism). If diarrhea occurs with hyperthyroidism, a low-fiber diet may help.
- Hydrate well to aid digestion, and consider probiotics to help maintain gut health.
8. Puffy Face and Swollen Neck (Goiter)

Notice a swelling in your neck or a puffy face in the mirror?
- A goiter, or thyroid gland enlargement, may be visible as a lump.
- It can cause tightness in the throat or difficulty swallowing.
Visual Cue: Always examine neck swelling from the side in natural light. Subtle bulges often go unnoticed for months.
What to Do:
- Thyroid treatment: Medications like levothyroxine (for hypothyroidism) or antithyroid drugs (for hyperthyroidism) can reduce swelling in the neck.
- Iodine deficiency: If the goiter is caused by iodine deficiency, your doctor may recommend iodine supplementation or dietary adjustments (such as eating iodized salt).
- Surgery or radiation: In some cases, surgery to remove part of the thyroid or radioactive iodine treatment may be needed if the goiter is large and causing difficulty swallowing.
9. Slow Heart Rate or Palpitations
Heart acting up?
Thyroid issues can affect cardiovascular rhythm.
- Hypothyroidism may slow your heart rate.
- Hyperthyroidism may cause palpitations, fluttering, or rapid heartbeats.
Fascinating Link: The thyroid gland and heart are deeply connected—your heart actually has receptors for thyroid hormones!
What to Do:
- Thyroid hormone therapy: Hypothyroidism can slow the heart rate. Proper treatment can help restore normal heart function.
- Monitor heart health: If palpitations are related to hyperthyroidism, antithyroid medication, beta-blockers, or other treatments may be prescribed to control heart rate and prevent arrhythmias.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Avoid excessive caffeine or stimulants, which can exacerbate heart palpitations.
10. Dry Skin and Hoarseness
Dry, flaky skin and a raspy voice might not just be due to the weather.
- Reduced sweating in hypothyroidism causes dry, coarse skin.
- Swelling in the thyroid gland can press on vocal cords, leading to hoarseness.
Quick Check: Persistent hoarseness without infection or known cause? Get your thyroid checked.
What to Do:
- Thyroid treatment: Moisturizing dry skin can help, but treating the underlying thyroid imbalance will be key to long-term improvement.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to combat skin dryness.
- Humidify your home: Use a humidifier to maintain skin moisture levels in dry environments.
- Voice therapy: If hoarseness persists, see a specialist who can help restore vocal cord health.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you’re experiencing more than two of these symptoms consistently, it’s time for a full thyroid panel blood test. These symptoms often overlap with other conditions, but thyroid disorders are treatable—especially when caught early.
Important: Don’t self-diagnose based on symptoms alone. Always consult a healthcare provider.
Final Thoughts
Your thyroid may be small, but it influences nearly every system in your body—from your mood and metabolism to your menstrual cycle and mental clarity. Ignoring its cries for help can lead to bigger health issues down the road.
Think of it this way: Listening to your body isn’t paranoia—it’s prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the thyroid and why is it important?
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck. It produces hormones (T3 and T4) that regulate your metabolism, energy production, body temperature, and even your heart rate. A properly functioning thyroid is essential for maintaining balance in numerous bodily systems.
How is a thyroid problem diagnosed?
A thyroid disorder is typically diagnosed through blood tests that measure the levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Your doctor may also perform an ultrasound or biopsy if necessary to check for abnormalities like a goiter or nodules.
Can thyroid issues affect fertility?
Yes, thyroid imbalances can impact fertility. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt the menstrual cycle, making it more difficult to conceive. If you have thyroid issues and are trying to get pregnant, managing your thyroid health is crucial.
How long does it take to feel better after starting thyroid medication?
The effects of thyroid medication (like levothyroxine for hypothyroidism) can be felt within a few weeks to a couple of months. However, it may take several adjustments to find the right dosage for you. Be patient and stay in communication with your healthcare provider.
Are thyroid problems hereditary?
Yes, thyroid disorders can run in families. If someone in your family has a thyroid condition, you may be at higher risk for developing one yourself. Regular screenings can help catch any issues early.
Can thyroid problems cause depression or anxiety?
Yes, both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can impact your mental health. Low thyroid hormone levels are often linked to depression, while high thyroid hormone levels can cause anxiety and irritability. Treating the underlying thyroid issue can often alleviate these symptoms.
Is iodine important for thyroid health?
Yes, iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. A deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism or goiter. However, most people in developed countries get enough iodine through iodized salt and other dietary sources. If you suspect an iodine deficiency, consult with your doctor.





